What is the difference between multimode and singlemode fiber?
Although single mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber cable (MMF) are widely used in different infrastructures, the difference between single mode fiber and multimode fiber is still not clear for some people. Therefore, the following article will focus on the basic construction, blind distance, cost, etc. to make an in-depth comparison between SINGEL MODE and MULTI MODE fiber.
Overview of multimode and singlemode
Single mode means that the fiber can transmit one type of light mode at the same time. While multi-mode means that the fiber can transmit multiple modes. The difference between single mode fiber and multimode fiber is mainly in the fiber core diameter, wavelength and light source, bandwidth, distance and cost.
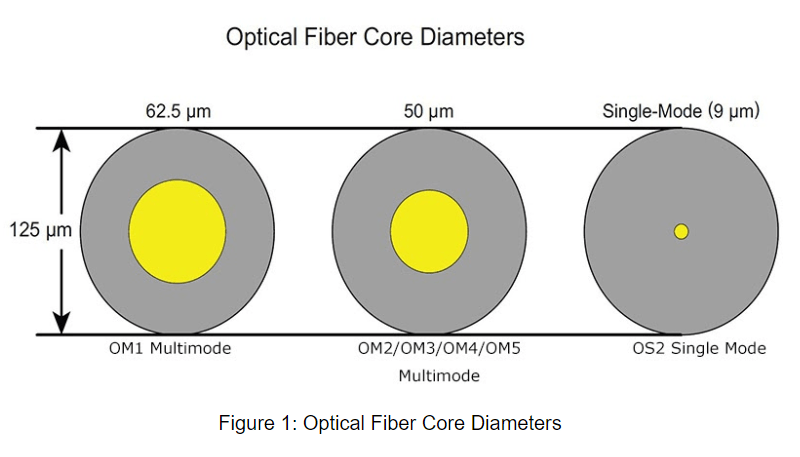
core diameter
The core diameter of single mode fiber is much smaller than that of multimode fiber. The diameter of its main core is 9 micrometers and the diameter of the multimode fiber core is 50 and 62.5 micrometers. Naturally, this allows you to have a higher “light gathering” ability and simplifies connections. The diameter of the single and multi cover is 125 micrometers.
The reception of multimode fiber is higher than that of SM fiber due to its larger core diameter. The fiber core of a single-mode cable is very narrow, so the light passing through these fiber optic cables is often not reflected, which minimizes reception.
| 9/125 Single Mode Fiber Simplex | 50/125 OM3 Multimode Fiber | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.36 dB/km | 850nm reception | 3.0 dB/km | ||||||||||||
| 0.22 dB/km | 1300nm reception | 1.0 dB/km | |||||||||||||
Wavelength
Due to the large size of the multimode fiber core, some low-cost light sources such as LEDs (light emitting diodes) and VCSELs (vertical emitting lasers) operating at 850nm and 1300nm wavelengths are used in multimode fiber cables. While single-mode fiber often uses lasers or laser diodes to generate light injected into the cable. And the commonly used single mode fiber wavelengths are 1310nm and 1550nm.
Bandwidth
The bandwidth of multimode fiber is limited by its optical mode, and the current maximum bandwidth is 28000 MHz * km of OM5 fiber. Whereas the bandwidth of single-mode fiber is theoretically unlimited because it allows only one mode of light to pass through at a time.
color core
As defined by the TIA-598C standard, for civilian applications, single-mode cable is covered with a yellow outer sheath and an orange or blue colored multi-core.
Multimode and singlemode fiber length
It has been recognized that single-mode fiber is suitable for long distances, while multimode optical fiber is designed for short distances.
| Fiber type | Fiber optic cable length | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fast Ethernet 100BA SE-FX | 1Gb Ethernet 1000BASE-SX | 1Gb Ethernet 1000BA SE-LX | 10Gb Base SE-SR | 25Gb Base SR-S | 40Gb Base SR4 | 100Gb Base SR10 | ||
| Single mode | OS2 | 200m | 5,000m | 5,000m | 10km | / | / | / |
| Multimode | OM1 | 200m | 275m | 550m (mode conditioning patch cable required) | / | / | / | / |
| OM2 | 200m | 550m | / | / | / | / | ||
| OM3 | 200m | 550m | 300m | 70m | 100m | 100m | ||
| OM4 | 200m | 550m | 400m | 100m | 150m | 150m | ||
| OM5 | 200m | 550m | 300m | 100m | 400m | 400m | ||
From the table above, it can be understood that the distance of single mode fiber is much longer than multimode fiber cables, but OM3 / OM4 / OM5 multimode fiber supports higher data rates. Because multimode optical fiber has a large core size and supports more than one light mode, its fiber distance is limited by mode dispersion, which is a common phenomenon in multimode fiber. While single mode fiber is not. This is the main difference between them. In addition, OS2 single-mode fiber can support longer distances in 40G and 100G connections.
The price of implementing communication with multimode fiber compared to single mode
The cost of the optical receiver compared to single mode fiber receivers, the price of multimode fiber receivers is almost two or three times lower.
Eriont is a manufacturer of single-mode and multi-mode optical receivers and transmitters in Iran.