The difference between G.652 and G.655 fibers
ITU-T G.65x optical fiber is a single-mode fiber standard series that is more popular and known and can be called G.652, G.653, G.654, G.655, G.656 and G.657 split, among which G.652 and G.655 are the two options that are usually used more. What is the difference between G.652 fiber and G.655 fiber and how to choose the better option between them?
Basics and models of G.652 and G.655
The first G.652 fiber model was introduced in 1984 and now this standard has four sub-sets: G.652.A, G.652.B, G.652.C and G.652.D. The size of four different G.652 cores is 8-10 micrometers. Meanwhile, G.652.C and G.652.D fibers have higher performance than G.652.A and G.652.B.
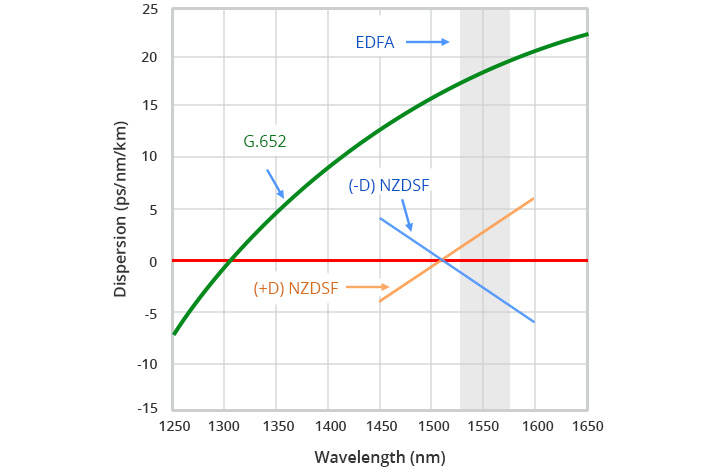
In the G.652 models, the core (core) G.652.A and G.652.B are designed to have near-zero dispersion at 1310nm wavelength – so this model is optimized to work in the 1310nm band. to be Due to the sputtering nature, both are not suitable for Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) applications. The more advanced fiber types G.652.C and G.652.D provide better performance in the wavelength region between 1310nm and 1625nm to support CWDM. Below is:
| G.652.A | G.652.B | G.652.C | G.652.D | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wavelength range | 1310nm-1550nm | 1310nm-1625nm | 1310nm-1625nm | 1310nm-1625nm |
| Maximum loss coefficient | 1310nm: 0.5dB/km 1550nm:0.4dB/km | 1310nm: 0.4dB/km 1550nm: 0.35dB/km 1625nm: 0.4dB/km | 1310nm to 1625nm: 0.4dB/km 1383 nm ± 3 nm: 0.4dB/km 1550nm: 0.3dB/km | 1310nm to1625nm: 0.4dB/km 1383nm± 3nm:0.4dB/km 1530-1565nm: 0.3dB/km |
| Application | 10G, 40G, 10G up to 40km | 10G | Similar to G.652.A. However, transmission bands extended to E, S and L. Suitable for CWDM systems | Similar to G.652.B. However, transmission bands extended to E and S. Suitable for CWDM systems |
The E band ranges from 1360nm to 1460nm.
S band refers to the wavelength range from 1460nm to 1530nm.
C band is a normal band whose wavelength is from 1530nm to 1565nm.
L band shows the wavelength range from 1565nm to 1625nm
G.655 standard can be divided into five types G.655.A, G.655.B, G.655.C, G.655.D and G.655.E, of which G.655 C / D / E are commonly used. G.655 single-mode fiber is known as zero-dispersion non-zero fiber (NZDSF) due to its dispersion at 1550 nm wavelength – close to zero but not yet zero. There are two types of NZDSF: (-D) NZDSF and (+D) NZDSF, which are on a negative and positive slope versus wavelength, respectively.
The specifications of the three types of G.655 that are often used are as follows:
| مدل | G.655.C | G.655.D | G.655.E |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | 1550-1625nm | 1550-1625nm | 1550-1625nm |
| Maximum Attenuation Coefficient | 1550nm: 0.35dB/km 1625nm: 0.4dB/km | 1550nm: 0.35dB/km 1625nm: 0.4dB/km | 1550nm: 0.35dB/km 1625nm: 0.4dB/km |
| Application | (1) Proposed G.691, G.959.1, and G.693.(2) For DWDM systems, channel spacings defined in G.694.1 are supported, depending on the minimum dispersion that is selected. | (1) For wavelengths greater than 1530 nm, the applications mentioned in G.655.C are supported.(2) For wavelengths less than 1530 nm, the fiber can be used to support CWDM applications at channels from 1471nm and higher. | (1) The same style as G.655.D, but with higher values especially for some small channel spacings.(2) The applications mentioned in G.655.C are supported. |
How to choose the best between G.652 and G.655 SMF cables?
The G.652 standard is designed for LAN, MAN, access and CWDM transmission networks. CWDM is an economically viable option, often used for short-haul applications on G.652-core cables, where signal amplification is not required. G.655 is the second most common type of fiber in terrestrial networks and has been widely used in long distance networks and DWDM transmission.
Choosing a single mode fiber optic cable depends on your needs. Core G.652 and its complementary version G.657 is a low-cost core standard and suitable for organizations and companies that do not need a speed higher than 10 Gbps with short distances. G.652 is recommended for these types of cases. If your desired bandwidth is higher than 10Gbps or requires long-distance support with higher performance, G.655 can be a better solution regardless of the much higher cost. The diagram below shows the applications of CWDM / DWDM G.652 and G.655.
| 10G CWDM | 40G CWDM | 10G DWDM | 40G DWDM | 100G DWDM | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G.652 | √ | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| G.655 | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |